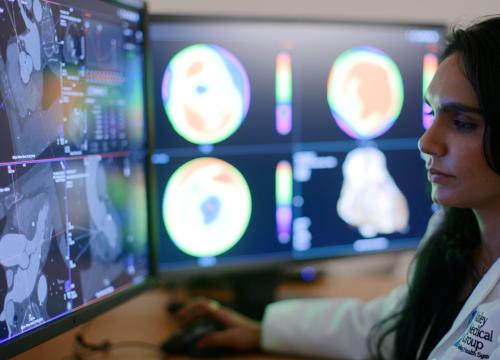
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease in the United States as noted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This condition is commonly detected through imaging after a patient expresses symptoms of chest pain or shortness of breath. In severe cases, the first sign of CAD is a heart attack.
Diagnostic approaches used for patients with non-acute chest pain vary based on clinician preference. To streamline the diagnostic phase, mitigate avoidable risks, and ensure high-quality care that addresses patient’s concerns, we turn to the findings of the Prospective Randomized Trial of the Optimal Evaluation of Cardiac Symptoms and Revascularization (PRECISE) Trial, funded by HeartFlow, Inc.
The PRECISE Trial looked to compare a “precision” diagnostic pathway (risk scoring and coronary computed tomographic angiography (cCTA) with selective fractional zow reserve (FFRCT)) usual care where the participant's care team selected specific noninvasive stress test or invasive test among a group of participants with stable chest pain and a clinical recommendation for testing suspected CAD. More than 2,000 patients were enrolled in the study, participating at 1 of 65 international sites.
The investigation began with a pre-test risk assessment using the PROMISE Minimal Risk Tool, which assigned participants a diagnostic strategy. Strategies included:
- Deferred testing for low-risk patients
- cCTA with selective FFR for elevated-risk patients. For the usual testing group, all risk levels underwent functional testing or direct invasive catheterization. Modality for testing was selected by the site clinician.
The findings from the PRECISE trial highlight the Precision strategy as the preferred diagnostic strategy when evaluating patients with stable chest pain and suspected coronary artery disease.
At The Valley Heart and Vascular Institute, our Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging team is using the latest computed tomography (CT) technologies, including HeartFlow® Analysis to perform a physiological assessment of coronary artery blockages in select patients. HeartFlow Analysis creates a digital 3D rendering of the patient’s coronary arteries and uses powerful computer algorithms to simulate blood flow to assess the impact of blockages. This approach allows for appropriate use of interventional procedures. Our interventional cardiologists use this technique to guide their invasive management, as it provides a clearer understanding of coronary artery disease, improves patient safety and outcomes, and reduces procedural duration.
To learn more about Valley’s use of CT technologies, visit ValleyHealth.com/CardiacImaging.